Advanced cold rolling work rolls are critical components in the production of high-strength and ultra-high-strength steel sheets, especially for demanding applications such as automotive body panels, electrical silicon steel, and stainless steel grades. Conventional 5% Cr cold work rolls often fall short in wear resistance, shape control, and surface roughness retention—leading to frequent roll changes, inconsistent strip quality, and elevated operational costs. To address these challenges, a next-generation cold-rolled work roll has been engineered through precise alloy design and advanced manufacturing protocols, delivering measurable improvements in performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency.
Why High-Strength Steel Demands Advanced Cold Mill Rolls
In modern cold rolling mills, the increasing strength levels of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS)—ranging from DP600 to DP1180 and beyond—exert extreme mechanical and thermal loads on work rolls. Standard cold mill rolls suffer from rapid surface degradation, spalling, and loss of crown control, which directly impacts flatness, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy of the final product. This bottleneck necessitates the development of cold rolling mill rolls with enhanced matrix strength, refined carbide architecture, and superior tempering stability.
1. Material Design: Optimizing Alloy Chemistry for Performance
The foundation of the new advanced cold rolling work roll lies in its tailored microstructure. The base remains an iron-based martensitic matrix, but key modifications significantly elevate performance:
- Solid-solution strengthening: Increased Si and Mn content enhances matrix hardness without compromising toughness—more effectively than traditional Cr, Mo, or V additions.
- Carbide engineering: Controlled ratios of Cr, Mo, and V promote formation of fine, spherical M₇C₃ and MC carbides that resist fracture and delamination under cyclic loading.
Quantitative analysis of the carbide phases reveals:
| Carbide Type | Morphology | Diameter (μm) | EDS Composition (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M₇C₃ | Spherical | 100–1000 | 54Fe–37Cr–7V–2Mo |
| MC | Spherical | 30–200 | 83V–12Cr–2.5Mo–2.5Fe |
2. Precision Manufacturing Process
From raw material to finished roll, every step is tightly controlled to ensure structural integrity and performance consistency:
- Melting & Refining: Electric arc furnace → LF refining → VD vacuum degassing → electrode casting under argon protection → electroslag remelting (ESR) with controlled melt rate.
- Homogenization & Forging: ESR ingots undergo 1200°C homogenization to dissolve coarse carbides, followed by multi-pass upsetting and elongation forging to achieve full density and grain refinement.
- Heat Treatments:
- Post-forging: Normalizing + spheroidizing anneal to reduce hydrogen and stabilize structure.
- Preparatory: Quenching and tempering to optimize core properties and prepare for final hardening.
- Final: Dual-frequency induction hardening for deep, uniform case depth (≥15 mm), followed by low-temperature tempering in atmospheric circulation furnaces.
- Quality Assurance: Ultrasonic testing, macro/microstructural inspection, gas analysis (H₂ < 2 ppm), and inclusion rating per ASTM E45 ensure only defect-free billets proceed.
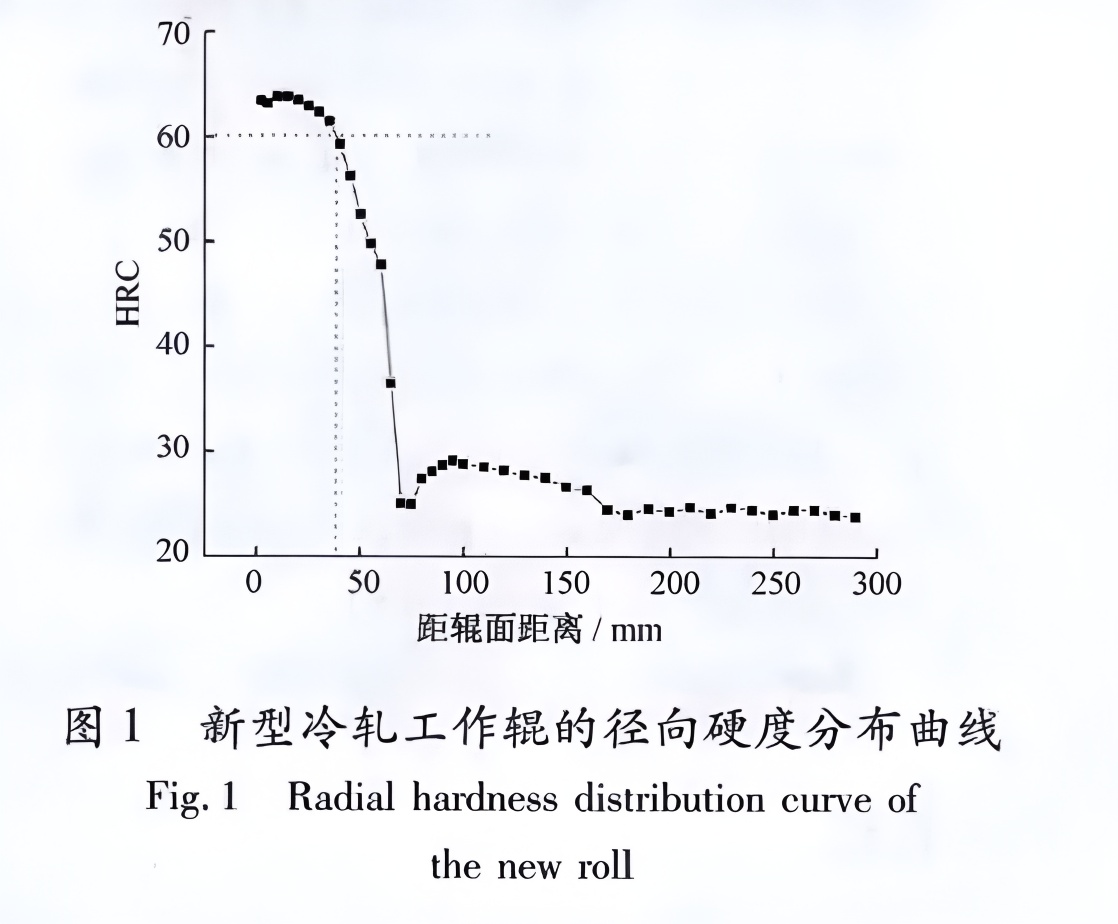
3. Radial Hardness Profile and Microstructure
The radial hardness distribution (see Figure 1) demonstrates a hardened working layer (>HRC 63) extending ~15 mm below the surface. Below this, a transition zone (~40–70 mm depth) contains minor lower bainite with hardness dropping to HRC 55–60. At ~70 mm depth, the structure transitions to spheroidized pearlite (HRC ~25), while the core (>75 mm) consists of tempered sorbite and spheroidized pearlite (HRC 25–29), ensuring excellent roll body toughness.
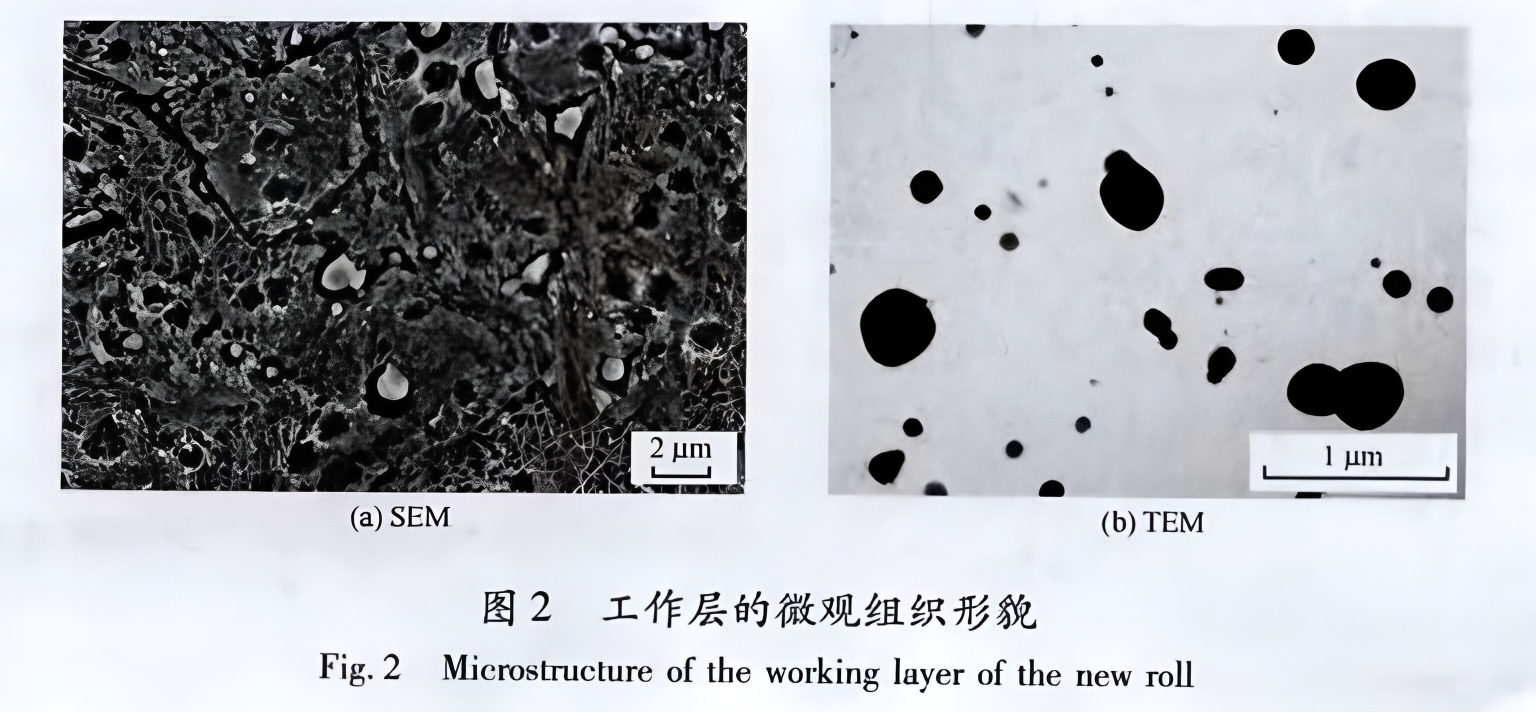
4. Mechanical and Wear Performance Comparison
Comprehensive testing confirms the superiority of the new roll over conventional 5% Cr counterparts:
| Property | New Work Rolls | Conventional 5% Cr Rolls |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 772.5 | 665.0 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 1060 | 955 |
| Elongation (%) | 15.0 | 16.5 |
| Reduction of Area (%) | 36.25 | 42.50 |
| Impact Energy (J) | 12.7 | 9.0 |
Wear resistance was evaluated via ring-block tests (1000 N load, 200 rpm, oil-lubricated, 2 hours):
| Sample | Avg. Wear Volume (mm³) | Hardness Before (HRC) | Hardness After (HRC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Work Rolls | 0.0530 | 63.1 | 63.1 |
| Conventional 5% Cr Rolls | 0.1060 | 64.0 | 63.5 |
The new roll exhibits **~50% lower wear volume** and **zero hardness drop**, confirming exceptional tempering stability—critical for maintaining surface texture and roughness during extended rolling campaigns.
5. Field Validation in High-Strength Steel Production
Four prototype rolls were deployed over six months in Baosteel’s temper mill for high-strength automotive steel (DP780–DP980). Under identical operating conditions—including standard grinding cycles, chrome plating, and surface texturing—the new rolls outperformed six imported benchmark rolls:
- 40% higher average single-cycle rolling tonnage (from 18,000 t to 25,200 t per roll set)
- 7% reduction in grinding depth per removal, extending total roll life
- Consistent strip flatness (<0.5 I-Unit) and surface roughness (Ra = 0.8–1.2 μm)
This real-world validation confirms the roll’s suitability not only for AHSS but also for other hard-to-roll materials like grain-oriented silicon steel and austenitic stainless steel.
Conclusion: A New Benchmark for Cold Rolling Mill Rolls
By integrating advanced alloy design, precision ESR processing, and dual-frequency induction hardening, this new generation of cold rolling mill rolls delivers unmatched performance in high-strength steel production. Key advantages include:
- Enhanced matrix strength via Si/Mn solid-solution hardening
- Optimized carbide size, distribution, and composition for wear resistance
- Superior toughness and impact resistance in the roll body
- Extended service life and reduced grinding consumption
- Compatibility with existing mill infrastructure and maintenance protocols
For steel producers targeting premium-grade cold-rolled products, these advanced work rolls represent a strategic upgrade—reducing cost-per-ton, improving yield, and enabling stable production of next-generation high-strength materials.

Keywords for SEO: cold rolling mill rolls, work rolls, rolling mill roll material, forged steel work rolls, tungsten carbide rolls for rolling mills

